Internal Control Department
For more details see: Internal Control Department
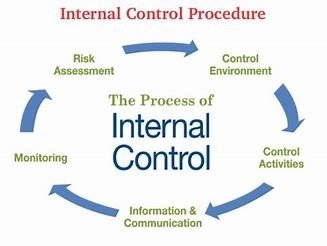
What are internal controls and why are they important?
Internal controls are the procedures put in place to help achieve the objectives of the university related to financial, strategic, and academic initiatives. Good controls encourage efficiency, compliance with laws, regulations and university policies, and seek to eliminate fraud and abuse.
Some everyday internal control procedures include:
· Locking your office when you step away from your desk
· Reviewing monthly comptroller's statement to verify transactions
· Requiring authorization on certain documents
· Most internal controls can be classified as preventive or detective. Preventive controls are designed to avoid errors or irregularities from occurring initially.
A few examples are:
· Reading and understanding University Policies and Procedures, such as timekeeping requirements for hourly employees helps prevent violations of the Federal Fair Labor Standards Act.
· Detective controls are designed to identify an error or irregularity after it has occurred. These controls are performed on a routine basis to identify any issues that pose potential risks to the University on a timely basis.
· Taking an annual physical inventory of computer equipment stored in a particular place will determine if any items have been misplaced or stolen.
· Establishing effective internal controls can help a department operate more efficiently and effectively and provide a reasonable level of assurance that the processes and products for which it is responsible are adequately protected.
Employees' Role in Internal Controls:
Everyone within the University has some role in internal controls. An individual’s responsibility depends mainly on the level of involvement at the university. senior administrators establish the presence of integrity, ethics, competence and a positive control environment. The department directors and managers are responsible for establishing and maintaining internal controls within their departments. Other department personnel are responsible for executing control policies and procedures established by department heads.
.png)